Semantic SEO is no longer just a buzzword—it’s the future of search engine optimization. As algorithms evolve, understanding the meaning behind search queries becomes critical for anyone aiming to rank higher on Google. But what exactly is Semantic SEO, and how can it transform the way your website performs in 2024?
OctopusWriters dives deep into this groundbreaking approach, revealing how it can drastically improve your rankings, traffic, and overall online presence. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to fine-tune your existing strategy, this guide will unlock the power of Semantic SEO for website success.
Want to know about what this shift means for your site? Let’s explore how mastering these techniques will future-proof your digital strategy.
Semantic SEO
Semantic search is the way search engines interpret and connect keywords with the user’s intent behind a search query. It represents a significant evolution from earlier methods where search engines, like Google, operated mainly as “matchmakers.” In the past, these engines would pair the exact words in a query with identical words found on webpages, offering straightforward but often shallow results.

The introduction of semantic search revolutionized this process. Now, search engines understand natural language, recognizing the true intent behind a query. For instance, when you search for “pizza near me” at 11 p.m., the search engine doesn’t just provide a list of pizza places. Instead, it prioritizes restaurants that are open late or offer night delivery, recognizing the time-sensitive nature of your request.
This new method contrasts sharply with exact-match search (or lexical search), where only exact matches of words are considered, ignoring spelling variations or grammatical differences. Semantic search, however, delves deeper—using sophisticated algorithms to interpret and fulfill the nuanced needs of users. This results in more relevant, accurate, and intuitive search experiences.
What is semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO involves creating content with greater meaning and depth, helping search engines like Google understand your content beyond just matching keywords. Gone are the days when top rankings could be achieved by simply repeating the same keyword multiple times. Today, search engines prioritize content that is not only relevant to the initial query but also addresses related questions a user may have after reading the content.
For example, if someone searches for “Semantic SEO,” they expect more than just a simple definition. They want comprehensive information, such as how it works, how to optimize for it, and its benefits. A well-optimized article for Semantic SEO covers all relevant aspects of a search query, delivering a richer, more meaningful user experience.
This shift began in 2011, when search engines started using artificial intelligence and natural language processing to better understand search intent. Instead of focusing solely on exact keyword matches, they began analyzing concepts and entities.
By using semantic SEO techniques such as schema, SEOs can enhance how search engines perceive the quality of their content, improving its chances of ranking higher in search results.
How semantic SEO has transformed Google’s ranking
In the early days of SEO, Google’s ranking algorithm was quite basic. Its crawlers would primarily focus on finding exact keywords on a webpage to determine relevance. However, human language is much more complex than just individual words. Context, tone, and even the surrounding paragraphs play significant roles in understanding meaning.
To keep up with this complexity, Google has progressively shifted towards a more semantic and human-like approach to interpreting and ranking content.
Key milestones in this evolution include:
- Knowledge Graph: Google’s vast knowledge base that helps its crawlers understand relationships between entities and concepts.
- Hummingbird (2013): This algorithm update allowed Google to better understand the intent behind queries, reducing the focus on singular keywords and emphasizing the overall meaning.
- RankBrain (2015): A machine learning algorithm that helps Google process user intent and deliver more relevant search results based on context.
These advancements enable Google to not only recognize the primary topic of a piece of content but also understand how related subtopics and terms interconnect, offering more accurate and meaningful search results.
How semantic SEO enhances the user search experience
Why is there such a strong focus on semantic SEO?
Google’s primary goal is to improve the search experience for users. People don’t typically seek just one simple answer; they often want a deeper understanding of the topic they are researching.
For instance, if someone searches for “what are backlinks?”, they are likely to have additional follow-up questions such as:
- How do I get backlinks?
- How many backlinks are necessary?
- Can I buy backlinks?
- What’s the difference between white hat and black hat backlinks?
Instead of making users click through multiple articles to find these answers, semantic SEO helps ensure that a single piece of content covers all these related topics. This not only saves time but also creates a more seamless, informative experience for users.
By addressing a range of relevant questions in one place, semantic SEO allows users to dive deeper into a topic without constantly returning to the search bar. Ultimately, this approach enhances the overall search journey, making it more intuitive and efficient.
How semantic SEO leverages entities
A key component of semantic SEO is the concept of entities. These can be people, places, organizations, or any distinct idea or object that holds meaning. By incorporating entities into search algorithms, search engines like Google can better understand the relationships and context surrounding these entities, leading to more accurate and relevant search results.
Entities enable search engines to move beyond simple keyword matching to grasp the intent behind a query. For instance, if someone searches for “apple,” search engines can determine whether the user is looking for the fruit or the tech company based on the surrounding context and other related entities.
Google organizes and connects entities through its Knowledge Graph, a framework that helps search engines map out these relationships. From an SEO standpoint, understanding and incorporating entities into your content, meta tags, and structured data is crucial for giving search engines the context they need. This improves content relevance and visibility in search results.
As voice search and natural language processing gain popularity, the role of entities becomes even more significant. Conversational queries, especially through voice search, rely heavily on context, and entities help search engines interpret and respond accurately. Some experts even suggest that Google may be shifting from mobile-first indexing to entity-first indexing, where the hierarchy of entities in the Knowledge Graph plays a primary role in search rankings.
What are the benefits of semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO offers a range of significant benefits for businesses aiming to improve their online visibility and drive organic traffic. By leveraging semantic technologies and structured data, companies can enhance how search engines interpret and rank their content, leading to measurable improvements in performance.
For instance, structured data implementation can yield substantial growth in key metrics. In one case, a design-focused website experienced a 12.13% increase in new users, an 18.47% rise in organic traffic, and a 2.4X increase in page views after just three months of adopting semantic SEO strategies. This approach helps search engines better understand your content, making it more relevant to users and increasing the likelihood of converting visitors into customers.
Beyond these metrics, semantic SEO future-proofs your content against algorithm changes by focusing on user intent rather than individual keywords. This allows your website to rank for a broader range of related keywords and appear in rich SERP features like People Also Ask and rich snippets, further boosting your visibility. It also helps you send quality signals to Google by meeting their E-E-A-T standards (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), which improves your content’s credibility and rankings.
By focusing on meaningful, structured content, semantic SEO ensures that visitors stay on your site longer, engage more deeply, and ultimately convert at higher rates. This approach provides businesses with a strategic advantage in today’s search landscape, helping them stand out in search results and keep ahead of competitors.
How Can You Optimize Content For Semantic SEO?
How to optimize content for semantic SEO
Optimizing content for semantic SEO requires a strategic approach to make your content more meaningful and easier for search engines to interpret while ensuring it remains relevant to your audience. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you effectively optimize your web pages.
- Understand user intent: The first step is identifying what users are truly searching for and how search engines interpret those queries. By analyzing the intent behind a search, you can ensure your content aligns with what your audience expects to find.
- Identify entities and related concepts: Next, pinpoint the entities, topics, and related concepts relevant to the search query. This includes exploring opportunities for incorporating structured data to enhance how search engines understand your content.
- Optimize content coverage: Once you know the entities and topics, it’s essential to expand your content to comprehensively address these areas. Ensure the entities are naturally mentioned, and use internal links to connect related content across your site.
- Implement structured data: Add the appropriate markup to your page, providing search engines with clear, structured information about the entities and related concepts. This step is key for improving your visibility in rich snippets and other enhanced SERP features.
- Enhance traditional SEO elements: Finally, ensure all basic SEO elements—such as title tags, headings, alt text for images, and internal linking—are well-optimized. These foundational factors still play a significant role in improving your search rankings.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your content not only aligns with user intent but is also optimized for the semantic web, improving your chances of ranking higher and attracting more relevant traffic.
Is the web ready for semantic SEO?
A semantic web doesn’t simply mean stuffing pages with synonyms or semantically related words. As Tim Berners-Lee described it, the semantic web is an extension of the current web, providing information with well-defined meaning that allows humans and machines to collaborate more effectively.
The launch of schema.org in 2011 was a pivotal moment in making the web more semantic. Shortly after, Google’s SVP of Engineering, Amit Singhal, introduced a groundbreaking concept with the Knowledge Graph, shifting the focus from keywords to real-world entities. He explained how queries like “Taj Mahal” could refer to a monument, a musician, or a casino, highlighting the need for search engines to understand the deeper meaning behind words.
The Knowledge Graph was a major advancement toward enabling search engines to interpret queries the way humans do, allowing us to search for things, people, or places rather than just strings of text. This shift is a crucial step in the evolution of semantic SEO, which aims to make search smarter by understanding the context and relationships behind the words we use.
Challenges and limitations of semantic SEO
While semantic SEO offers considerable advantages, it comes with several challenges and limitations that website owners need to consider before fully adopting it.
- Complexity: Implementing semantic SEO is not straightforward. It involves advanced techniques such as semantic markup, natural language processing, and algorithms to analyze and understand content. The technical nature of these elements can make it difficult for some website owners to grasp and apply effectively.
- Limited adoption: Despite its growing importance, semantic SEO has yet to be fully embraced by many website owners and search engines. Not all search engines are equipped to interpret semantic markup and natural language techniques effectively, which can limit the overall impact of semantic SEO efforts.
- Limited scope: While semantic SEO enhances search relevance and accuracy, it is just one factor in a website’s success. Elements like design, user experience, and marketing are equally important for driving visibility and traffic. Therefore, semantic SEO should be integrated as part of a broader SEO strategy, rather than being seen as a standalone solution.
- Changing algorithms: Search engines continuously update their algorithms to improve search results. As these changes occur, strategies used in semantic SEO may become outdated, requiring website owners to stay informed and adjust their approach to align with evolving search engine practices.
These challenges emphasize the need for a well-rounded approach to SEO, ensuring that semantic techniques are balanced with other essential elements of website optimization.
Future developments in semantic SEO
Despite the current challenges, semantic SEO is a rapidly growing field that is set to continue evolving in the coming years. Here are some key areas where we can expect significant developments:
- Improved adoption: As more website owners and search engines recognize the benefits of semantic SEO, its adoption will likely increase. This could result in broader use of semantic markup and natural language processing to enhance the relevance and accuracy of search results.
- Enhanced functionality: As semantic SEO becomes more mainstream, the technologies and techniques will continue to improve. Future developments may include advanced algorithms like Heading Vectors or other tools that can analyze and understand website content more effectively, providing even more accurate search results.
- Integration with emerging technologies: We can expect semantic SEO to be more deeply integrated with other innovations, such as voice search, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. These advancements will help search engines handle more complex queries and improve the accuracy of voice search results.
- Greater focus on user experience: As the adoption of semantic SEO grows, there will likely be a stronger emphasis on improving user experience. This could involve personalizing search results based on a user’s location, interests, or previous search history, and providing more relevant and detailed information to enhance engagement.
Overall, semantic SEO is a rapidly evolving field with immense potential. As it becomes more widely adopted, we can expect continued improvements in search engine accuracy and a growing focus on leveraging these techniques to create a more user-centered experience.
How topic maps enhance semantic SEO
The web is becoming increasingly semantic, and SEO is evolving alongside it. As search engines grow more sophisticated in understanding and interpreting web content, the way we create content must also adapt. No longer is it enough to think in terms of individual webpages and keywords; instead, we must focus on the relationships between concepts.
Ted Nelson, a pioneer of the internet, coined the term intertwingularity, which represents the idea that everything is deeply interconnected. This concept challenges the traditional approach of organizing information into neat categories, emphasizing that all things are inherently linked.
In semantic SEO, search engines prioritize content by analyzing the relationships between ideas and calculating the distance between meaning vectors. To optimize for this, we need to build a content architecture that clearly communicates these relationships. This is where topic maps come into play.
Topic maps serve as a blueprint for structuring content, helping you determine what topics to cover and how to interconnect them. By creating well-organized topic maps, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility and ranking on search engines like Google.
Understanding and mastering the creation of topic maps is essential for succeeding in today’s semantic search landscape.
What is a topic map?
A topic map is a visual representation of interconnected concepts and entities related to a central topic. It allows you to see the relationships between ideas, helping you identify which concepts have already been covered on your website and revealing opportunities for new content. By understanding these connections, you can create content that fills gaps and further enriches your site’s relevance.
In this context, a content model becomes vital to your SEO strategy. It helps both search engines and users understand the relationships within your content, improving visibility. Structuring your content with a strong model ensures search engines recognize your site among vast amounts of information, making it easier for users to find content that aligns with their search intent.
The more comprehensive and well-structured your content model, the better your chances of targeting the right audience. Using tools like WordLift, you can refine and build a Knowledge Graph that highlights the most relevant aspects of your business, drawing attention to the key information that resonates with your audience and enhances your company’s online identity.
How to conduct semantic keyword research effectively
Semantic keyword research involves selecting and organizing keywords based on user intent, relevance, and their relationships to each other. This process allows you to create more targeted, meaningful content that aligns with both search engines and users. Let’s explore a step-by-step action plan for optimizing your semantic keyword research.
Create a keyword list
Start by compiling a list of related keyphrases and LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords. These keywords are semantically related to your target keyphrase, helping search engines better understand your content’s meaning.
Identify long-tail keywords
Next, focus on long-tail keywords—these are longer, specific queries that reflect clear user intent. For example, instead of targeting broad terms like “yoga poses,” aim for long-tail keywords such as “beginner yoga poses for flexibility” or “how to do a downward-facing dog pose.” Long-tail keywords are usually less competitive and more aligned with user needs.
Structure your keyword list
After gathering keywords, organize them into groups. This process, known as keyword clustering, groups similar queries together. For example, you can cluster keywords related to yoga poses into categories like “yoga postures,” “yoga asanas,” or “yoga beginner poses.” Grouping keywords by relevance, search volume, and user intent is a vital part of your semantic SEO strategy.
Using Google to build your keyword list
Google is a great starting point for collecting semantic keyword data. Begin by entering your primary keywords into the search bar. For instance, if you run a yoga studio, you may want to rank for commercial keywords like “yoga studio LA” or informational keywords like “benefits of meditation.” Google provides valuable keyword suggestions as you type, based on trending topics and your search history.
Leverage Google suggestions
Don’t overlook long-tail keywords—these are often in the form of questions or complete phrases. For example, typing “yoga” may reveal suggestions like “yoga for beginners” or “yoga for back pain.”
Explore the “People also ask” section
Another useful area is the “People also ask” section, where Google lists common questions related to your query. These can be valuable sources of inspiration for long-tail keywords that users are actively searching for.
Use related search terms
At the bottom of Google’s first results page, you’ll find related search queries. This is another way to uncover long-tail keywords that are relevant to your topic. These search queries are great for expanding your keyword list.
Find synonyms and LSI keywords
Google’s autocomplete feature and related search results can also help you identify synonyms and LSI keywords. These terms aren’t always direct synonyms but may be semantically linked. For example, “yoga asana” and “yoga pose” are synonyms, while “yoga class” is related but has a different meaning. Collecting these keywords enhances the depth of your content, making it more relevant to a wider audience.
Using keyword planner tools for deeper insights
To speed up the process and access more extensive data, you can use specialized keyword planner tools. These tools offer databases with billions of search queries, providing thousands of keyword ideas with just a few clicks. For example, a yoga-related query might return 450,000 monthly searches, giving you a sense of which keywords to prioritize.
These tools often allow you to apply filters to narrow down your keyword list. You can exclude high-volume, highly competitive keywords and focus on queries that are more specific to your niche. Additionally, use tabs like “Related,” “Questions,” and “Low-search volume” to find additional keyword variations and ideas.
Cluster your keywords
Once you’ve gathered all possible keywords, consolidate them into a spreadsheet and eliminate duplicates. From there, begin keyword clustering by grouping terms into different categories.
Group keywords by semantic relevance
For example, if you have several keywords related to “yoga asanas,” you can cluster them based on their semantic relationship. Terms like “yoga poses,” “yoga postures,” and “asana list” would fall into the same group.
Cluster by user intent
Another approach is to group keywords based on user intent. For example, queries like “how to do yoga asanas” and “what are beginner yoga poses” reflect informational intent and can be clustered together.
Cluster by search volume
Organizing keywords by search volume is also useful for structuring your site. High-volume keywords might serve as primary categories, while low-volume keywords can be used for blog posts, product pages, or specific service offerings.
Implementing content clusters with semantic SEO
Semantic SEO goes beyond individual keywords by focusing on content clusters based on topics. This method uses the pillar cluster model, where broader topics are supported by more specific subtopics, creating a well-organized content structure.
Apply the pillar cluster model
In this model, group keywords into topics for future pages. The pillar page serves as the main hub for the broader topic, while subtopic pages dive deeper into related concepts. These pages are linked together to help search engines understand the hierarchy and context of your content.
Build content hubs
Content hubs allow you to collect all related content in one place, making it easier for users to explore a comprehensive resource on a specific subject. The pillar page addresses the core topic, while thematic pages delve into the subtopics. These internal links help search engine bots comprehend the relationships and improve your overall search visibility.
By organizing your content using topic clusters and hubs, you’ll create a more cohesive and semantically rich website structure, enhancing both user experience and SEO performance.
In short, semantic keyword research is a powerful approach to developing content that not only aligns with search engine algorithms but also caters to user intent. Through proper keyword clustering and strategic content planning, you can significantly improve your website’s ranking and user engagement.
How to write content using semantic SEO
Writing content with semantic SEO involves following a few essential steps to ensure your content is both optimized for search engines and valuable for readers. Here’s how to approach it:
Start with thorough keyword research
Before you begin writing, it’s crucial to research and understand the keywords and phrases relevant to your topic. This step ensures that your content is aligned with search engine algorithms and increases your chances of ranking higher in search results.
Incorporate keywords naturally
Once you have your target keywords, the key is to integrate them naturally into your content. Avoid keyword stuffing, which involves overloading your page with keywords. This practice can harm your rankings instead of boosting them. Instead, use the keywords in a way that fits seamlessly into the flow of your writing.
Use related keywords and phrases
To further enhance your content, include related keywords and phrases that are semantically connected to your main topic. For example, if your primary keyword is “dog training,” related phrases could be “canine behavior,” “puppy training,” and “dog obedience.” These help search engines understand the broader context of your content, boosting relevance.
Implement structured data
Incorporating structured data is another vital aspect of semantic SEO. Structured data is code that you add to your website to help search engines better interpret the content. For instance, if you’re writing a recipe, you can use structured data to highlight details like ingredients, cooking time, and servings. This additional information helps search engines present your content more accurately in search results, improving your chances of ranking higher.
Focus on high-quality content
Technical optimization is important, but your content must also provide value to readers. Write in a clear and engaging style, making sure the content is informative and relevant. Use images, videos, or infographics to break up long sections of text and make the content visually appealing. Including internal and external links to relevant resources further enriches your content, offering additional value to readers.
13 best practices for semantic SEO
Publish topically relevant content
In a large-scale Google ranking factors study, it became clear how powerful topically relevant content is for SEO. But what does this term really mean, and how can you apply it to your content strategy?
Topically relevant content refers to in-depth coverage of a subject, providing more comprehensive information than the average post. For example, rather than writing a brief 500-word post titled “7 Ways to Optimize for Mobile SEO,” you should aim for a detailed guide that covers every aspect of the topic. By doing this, you create content that covers a subject thoroughly, which is more likely to rank higher in Google’s search results.
Write topic outlines
To ensure your content is topically relevant, it’s a good idea to create topic outlines before you begin writing. A topic outline lists all the subtopics you plan to cover in your content. This helps ensure that you’re addressing all aspects of the topic, which Google’s algorithms reward.
For example, when writing about backlinks, creating an outline that includes all subtopics like “types of backlinks,” “how to build backlinks,” and “backlink strategies” ensures that your content is comprehensive. This approach can help improve your chances of ranking higher for the main keyword.
Answer “people also ask” questions
A smart strategy for improving content relevance is to include answers to questions found in Google’s “People Also Ask” boxes. These boxes provide common user queries on a particular topic, and addressing them in your content helps you rank better not only for your primary keyword but also in these specific question boxes.
For instance, if you’re writing about backlinks and you notice a “People Also Ask” question like “What is a backlink example?”, including a clear example in your content helps optimize it for both the keyword and that related query.
Target keyword variations with the same page
In the past, SEO strategies focused on creating separate pages for every variation of a keyword. For example, one page would target “best cookie recipes” and another “best cookies recipe.” But with advancements like Google’s Hummingbird update, this practice is outdated.
Now, you can optimize a single page for multiple keyword variations. Google’s algorithms understand that similar phrases often refer to the same topic. For instance, one of my top-performing posts, “YouTube SEO: How to Rank YouTube Videos,” ranks for both “YouTube SEO” and “YouTube SEO 2024” on a single page, thanks to semantic SEO.
Avoid long-tail keywords
While long-tail keywords have long been favored for their lower competition, Google’s use of semantic SEO now means that similar long-tail keywords are often grouped under the same topic. Instead of targeting long-tail keywords individually, it’s more effective to focus on semi-competitive medium-tail keywords.
For example, targeting “keyword research” instead of highly specific long-tail keywords like “best keyword research techniques” allows your content to rank for a broader range of related terms. If your content is detailed and well-optimized, Google will automatically rank it for various related long-tail keywords.
Don’t ignore keywords altogether
While it’s true that Google’s algorithms now focus more on topics than individual keywords, that doesn’t mean you should stop targeting keywords entirely. Keywords are still important for helping search engines understand your content.
Google recommends continuing to use keywords strategically. The difference now is that you can target multiple keywords on a single page and expect Google to rank that page for both your primary keyword and related variations.
Publish long content
If you want to succeed with semantic SEO, producing long-form content is essential. By “long,” we’re talking about content that spans 1,000, 2,000, or even 5,000 words. However, the goal is not to pad your content with unnecessary fluff, but to thoroughly cover the topic in-depth.
It’s nearly impossible to provide comprehensive information on a subject in a short 400-word blog post. Depending on the complexity of the topic, several thousand words might be necessary to give readers the full picture—and that’s perfectly fine. For example, a detailed list of SEO tips that spans over 3,000 words can provide everything a user needs on a single page, enhancing the user experience.
From Google’s perspective, long, high-quality content that answers users’ queries is valuable. So, don’t hesitate to create in-depth articles; in fact, it can be a significant SEO competitive advantage.
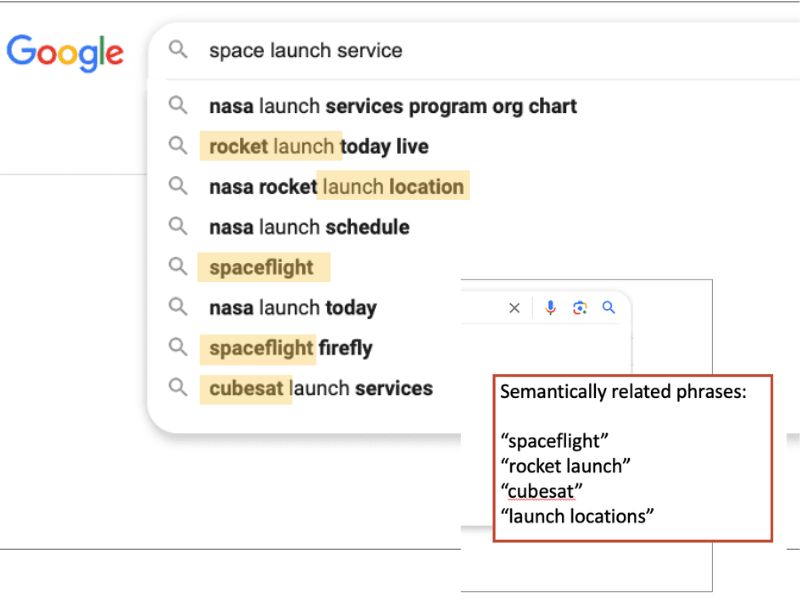
Include semantically related phrases
Also referred to as LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords, semantically related phrases help Google understand the broader context of your content. These terms are not just synonyms but words and phrases that are naturally associated with your main topic.
Using semantically related phrases in your content not only helps Google grasp your page’s overall theme but can also improve your chances of ranking for more long-tail searches. These keywords can enhance the semantic richness of your content, making it more relevant to a wider range of user queries.
Optimize for conversational keywords
With the rise of voice search, optimizing your content for conversational keywords is crucial. According to Google, 41% of U.S. adults perform at least one voice search per day, and these voice queries tend to be more natural and conversational. Voice search aligns perfectly with semantic search, which focuses on understanding topics rather than isolated keywords.
In the past, you may have forced awkward keywords like “link building tools SEO” into your content. Today, however, you can optimize for natural language versions, such as “link building tools for SEO,” and still rank well. This shift encourages writing in a more conversational tone that appeals to both users and search engines.
Use structured data
Structured data (Schema) provides an extra layer of context to your content, helping search engines better understand what your page is about. Although Schema doesn’t directly improve rankings, it supports semantic SEO by offering more information about your content to search engines.
Structured data can also increase the likelihood of your content appearing in rich snippets, which can boost your site’s organic click-through rate (CTR). While it’s not a ranking magic bullet, structured data is a useful tool to enhance how your content is displayed in search results, making it more appealing to users.
Internal linking
To enhance your semantic SEO efforts, internal linking is a powerful tool that connects your content across your website. A thoughtful internal link structure not only improves site navigation for users but also helps search engines better understand and rank your content.
A well-optimized internal link structure typically includes three key components:
- Menu link structure: These links are found in your website’s navigation and guide users to important pages.
- Breadcrumb link structure: These help users understand where they are within your site’s hierarchy and allow them to easily navigate back to previous pages.
- Internal link structures within the content: These are links embedded in the body of your articles, guiding readers to related content on your site.
By linking pages together, you enable search engines like Google to crawl and index your content more effectively. For instance, if your general “sneakers” page links to a more specific “kids sneakers” page, it can help Google understand the relevance and hierarchy of your pages. This can improve the visibility of your subcategory pages in search results for relevant queries.
To make the most of internal linking, it’s important to use relevant anchor texts. The anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink, which provides both users and search engines with information about the content on the linked page. In HTML, an anchor text looks like this:
| <a href=”https://www.example.com”>Anchor Text</a> |
Here are a few best practices for optimizing anchor texts:
- Use descriptive anchor text: The text should clearly describe the linked page’s content, helping users and search engines understand its relevance.
- Incorporate long-tail keywords: Including long-tail keywords in your anchor texts can make your internal links feel more natural and improve relevance for more specific search queries.
When implemented correctly, internal linking helps improve the visibility of your content, ensures users can navigate easily, and allows search engines to better crawl and index your site. A well-linked website builds strong semantic connections between pages, making your overall content strategy more effective.
Try to understand user intent
One of the most critical steps in optimizing content for semantic SEO is understanding the user intent behind a search query. Search engines like Google aim to provide users with a seamless experience by delivering content that fully satisfies their intent rather than offering disjointed or incomplete information.
To do this, you need to map out what the user is trying to achieve when they perform a search. For instance, if someone searches for “how to use WordPress,” they are likely seeking more than just basic instructions. They may also want to know:
- What are the benefits of using WordPress?
- Is WordPress better than other CMSs?
- What are the best plugins and themes for WordPress?
- How much does it cost to use WordPress?
- How to design a website with WordPress?
- Which domain and hosting options are best for WordPress?
By anticipating these additional needs and addressing them in your content, you create a more satisfying experience for the user. Instead of bouncing between multiple pages, they can get all the information they need in one place, which enhances the user experience and improves your chances of ranking higher in search results.
Create detailed content
When it comes to semantic SEO, detailed content is key. While the length of your content isn’t an official ranking factor, longer, well-structured content often signals to search engines that you’re covering the topic comprehensively. However, extending content length by stuffing it with keywords or repetitive phrases won’t be effective.
So, how do you create detailed content? One approach is to analyze the top-ranking pages for your topic in search engines. By reviewing how much information they provide, you can gauge how much detail your content needs to cover to meet user expectations.
Another useful tool is Answer The Public. For example, if you’re writing about “Semantic SEO,” you can use this tool to find over 40 questions related to the topic. While not all questions will be relevant, many will offer valuable insights into what users are looking for, allowing you to craft in-depth, comprehensive content.
This level of detail is essential for optimizing your content for semantic SEO. It ensures that your content addresses multiple facets of the topic, making it more valuable for both users and search engines.
Natural language processing and semantic SEO
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interact with human languages. NLP involves analyzing, interpreting, and generating natural language data to help computers understand and communicate more effectively with people.
In the context of semantic SEO, NLP plays a vital role by allowing search engines to grasp the meaning and context behind the content on websites. Traditionally, search engines relied on keyword-based algorithms, ranking pages primarily by the frequency of relevant keywords. However, this method has its limitations as it often fails to understand the actual context or purpose of the content.
With semantic SEO, NLP allows search engines to go beyond mere keywords and focus on the context and intent of a query. For instance, if a user searches for “best Italian restaurants in New York City,” an NLP-powered semantic SEO algorithm understands the intent behind the search and ranks websites focused on Italian restaurants in NYC, rather than simply matching individual keywords.
To implement semantic SEO effectively, websites need to incorporate structured data like schema.org. This additional layer of information helps search engines better understand the content’s context and meaning, ultimately improving the accuracy of search results.
Moreover, semantic SEO algorithms use machine learning to continuously improve their understanding of human language. By processing vast amounts of data, these algorithms learn to recognize language nuances and provide more precise and relevant search results over time.
Named entity extraction for semantic SEO
Named entity extraction is an essential technique in semantic SEO that focuses on identifying and extracting key entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, from a piece of content. This process helps search engines better understand the context and improve the ranking and relevance of web pages.
The primary advantage of named entity extraction is that it enables search engines to grasp the core themes and topic clusters of a webpage. By recognizing important entities, search engines can categorize the content more accurately, allowing for better search result rankings. This technique is especially valuable for websites that cover diverse topics, as it helps search engines identify the central focus of each page and deliver more relevant results to users.
In addition to improving rankings, named entity extraction enhances the overall understanding of website content. By extracting entities like people, organizations, and locations, search engines can provide users with additional context. For instance, if a webpage mentions a famous person, the process can identify the individual and offer related details, such as their profession or background.
Named entity extraction is also useful for disambiguating terms with multiple meanings. For example, if the word “Paris” appears in a text, the extraction process determines whether it refers to the city in France, Paris Hilton, or the mythological figure Paris of Troy. This helps search engines deliver more accurate and relevant search results.
By leveraging named entity extraction, websites can improve their visibility in search results and ensure that search engines deliver more precise content to users.
4 popular and free tools for semantic SEO
While no single free tool can fully manage your site’s semantic SEO, several tools can help you handle different aspects of the optimization process. Below are four popular tools you can use to improve your content’s semantic relevance.
Google autocomplete
Most bloggers are already familiar with Google autocomplete, but it’s also a valuable tool for discovering semantic keywords. Simply type a keyword into the search bar, and Google will provide a list of autocomplete suggestions based on popular searches. These suggestions often reveal related terms and user queries that can inform your content strategy.
Google related searches
Another useful feature is Google related searches, which can help you find LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing keywords) for your main topic. After typing your primary keyword into Google, scroll down to the bottom of the search results page. There, you’ll find a list of related searches that can be used to expand your content and cover more semantic keywords.

Answer The Public
We’ve already discussed Answer The Public, a tool that is excellent for generating semantic keywords. Just enter your primary keyword, and it will display a list of related questions and phrases people are searching for. This tool helps you cover all the angles and subtopics associated with your main keyword, ensuring your content is comprehensive.
Ubersuggest
Ubersuggest is another powerful, free tool that can assist with semantic SEO. It provides keyword suggestions based on your target keyword and shows search volume, competition, and other valuable metrics. Ubersuggest also suggests related keywords and content ideas, helping you identify semantic opportunities to optimize your content further. By using Ubersuggest, you can uncover long-tail and semantically related keywords that enhance your overall SEO strategy.
By leveraging these tools together, you can optimize your content for semantic SEO and create a more comprehensive and relevant experience for your users and search engines.
Semantic SEO – Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of semantic search?
Semantic search provides more relevant and accurate search results by understanding the intent behind a user’s query, rather than just matching keywords. This leads to better user satisfaction, increased page visibility, and higher search engine rankings for content that effectively addresses user intent.
What is semantic SEO structure?
A semantic SEO structure focuses on organizing content based on topics and entities rather than individual keywords. It involves creating a hierarchy of related content, using internal linking and structured data, which helps search engines understand the relationships between different pieces of content.
Is Google a semantic search engine?
Yes, Google is a semantic search engine. Over the years, Google has shifted from keyword-based search algorithms to semantic search, which allows it to understand the context and intent behind user queries, providing more accurate results.
Why is semantic SEO important?
Semantic SEO is important because it helps search engines better understand the meaning and context of your content. By optimizing for semantic search, you increase the likelihood of ranking for a variety of related queries, improve user experience, and stay competitive in a constantly evolving search landscape.
What is semantic search NLP?
Semantic search NLP (Natural Language Processing) is the process where search engines use NLP to understand and interpret the meaning behind user queries and website content. This allows search engines to deliver more relevant results based on context, rather than just matching specific keywords.
What is meant by semantic search?
Semantic search refers to the technique where search engines understand the meaning, relationships, and context behind search queries, rather than just focusing on individual keywords. It aims to deliver more accurate and user-friendly search results by interpreting the intent behind the query.
How did Google introduce semantic SEO?
Google introduced semantic SEO through updates like Hummingbird and the Knowledge Graph. These updates allowed Google to better understand the relationships between words, topics, and entities, enabling the search engine to deliver more relevant and context-driven search results.
Conclusions
Creating content using semantic SEO involves a blend of keyword research, natural keyword integration, related terms, structured data, and most importantly, high-quality writing. By following these guidelines, you’ll not only improve your rankings but also deliver more meaningful and engaging content for your audience, increasing both traffic and engagement on your site.
With tools and techniques evolving, it’s crucial to adapt your content strategy to meet user intent and provide comprehensive information. OctopusWriters emphasizes the importance of staying ahead of search engine updates by optimizing content that resonates with both search engines and users. By implementing semantic SEO best practices, your content will not only rank higher but also become a trusted resource in your niche, fostering long-term growth for your site.

