If you’re aiming to enhance and diversify your link profile, it’s essential to understand all the elements that contribute to it. One important aspect of this is “Nofollow Backlinks” As you explore various link-building strategies, you’ll likely encounter nofollow links. But what exactly are nofollow backlinks, and how can they benefit your website?

In this article, OctopusWriters will analyze what nofollow backlinks are and highlight the eight main advantages they offer to your business.
What Are Nofollow Backlinks?
Nofollow links are a specific type of hyperlink designed to instruct search engines not to pass on ranking value, also known as “link equity,” to the linked website. These links contain a special attribute in their HTML code: rel="nofollow"
By using the “nofollow” tag, you’re essentially telling Google and other search engines not to crawl the linked page or transfer any ranking authority to it. This is particularly useful when linking to untrusted or user-generated content, such as comments or external sources you don’t want to vouch for.
Here’s an example of how a nofollow link appears in HTML:
<a href="https://example.com/" rel="nofollow">Click here</a>`
The presence of the rel="nofollow" attribute within the hyperlink ensures that the link remains nofollow. While these links don’t pass SEO value, they still hold importance for driving traffic and maintaining a natural, diverse backlink profile.
How To Check Nofollow Backlinks
Now that you understand the key differences between NoFollow and DoFollow links, you’re probably eager to learn how to identify them. Fortunately, spotting the type of link is easy with just a few steps. Here’s how you can check whether a link is NoFollow or DoFollow on any website.
Step-By-Step Guide To Checking Links:
👉 Step 1: First, locate the hyperlink you want to investigate on the webpage.
👉 Step 2: Right-click on the link and choose “Inspect” from the dropdown options. This will launch the browser’s developer tools.
👉 Step 3: Review the HTML Code
The browser will highlight the HTML code corresponding to the link you selected. Look for the rel="nofollow" attribute in the code. If it’s present, the link is a NoFollow link. If the rel="nofollow" tag is absent, the link is DoFollow.
These three simple steps allow you to manually check any individual link. But what if you want to analyze all your backlinks at once? Instead of manually inspecting each one, you can use a variety of free tools that automatically scan and assess your link profile.
We’ll recommend some of these tools later in this article, so keep reading to learn more about NoFollow backlinks and how to manage them efficiently.
Example Of A Nofollow Link In HTML
Here’s what a NoFollow link looks like in HTML:
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Visit Example</a>
This snippet shows how the rel="nofollow" attribute is used to ensure the link doesn’t pass any SEO value to the destination page.
8 Key Benefits Of Having Nofollow Backlinks
While NoFollow backlinks don’t directly contribute to higher search engine rankings, they provide several indirect benefits that can be just as valuable for your website. Let’s explore eight advantages of having NoFollow backlinks.
Traffic And Visibility
Even though NoFollow links don’t pass link equity, they can still drive significant traffic to your site. If the link comes from a high-authority source, the visibility alone can attract a relevant audience, leading to potential conversions.
Expanding The Variety Of Links In Your Profile.
A well-rounded backlink profile includes a mix of DoFollow and NoFollow links. Search engines look for natural link-building patterns, and having both types of links ensures a balanced, diverse profile, which is essential for long-term SEO success.
Credibility And Authority
Being linked to by reputable sites, even with NoFollow links, can boost your site’s credibility and authority in your niche. These links signal to both users and search engines that your content is trustworthy and valuable.
Protection Against Penalties
NoFollow backlinks can protect your site from penalties associated with unnatural linking practices. A healthy backlink profile contains both DoFollow and NoFollow links, helping you avoid being flagged by search engines for manipulative tactics.
Brand Exposure
NoFollow links, especially those from prominent websites or social media platforms, can expose your brand to a wider audience. This increased visibility can result in more brand recognition and indirect benefits, such as increased mentions or even future DoFollow links.
Future Potential
What’s considered a NoFollow link today could have different implications in the future. By maintaining a balanced link profile now, you position yourself to benefit from any potential changes in search algorithms.
Relationship Building
Collaborating with influencers, bloggers, or other businesses through NoFollow links can foster strong relationships. These partnerships may lead to future opportunities, including DoFollow links or other collaborations that can further boost your online presence.
Testing And Experimentation
NoFollow backlinks allow you to experiment with different linking strategies without worrying about SEO penalties. This flexibility is great for testing content placement, outreach efforts, and user engagement to refine your digital marketing tactics.
While NoFollow backlinks might not directly influence rankings, their role in building traffic, relationships, and long-term brand value makes them an essential part of any well-rounded SEO strategy.
Why Was The Nofollow Tag Introduced By Search Engines?
The nofollow tag was initially introduced by Google to combat the growing issue of blog comment spam. As blogs became more popular, spammers exploited the comment sections by leaving links back to their own sites in an attempt to boost their rankings.
This tactic created two major issues:
- Spammy Sites Dominated Rankings: Low-quality, spam-filled sites began to rank well on Google, pushing high-quality websites out of the top search results.
- Uncontrolled Blog Spam: The strategy of using spammy links in blog comments worked so well that it quickly spiraled out of control, leading to an overwhelming amount of spam on blog posts.
To address this, Google introduced the nofollow tag in 2005 and incorporated it into their algorithm. The nofollow tag served as a way to prevent link spam from affecting search engine rankings. Soon after, other search engines like Bing and Yahoo also adopted the tag, making it a widely recognized tool in the fight against spammy link-building practices.
What Sets Nofollow Apart From Noindex?
Though the terms "nofollow" and "noindex" might seem similar, they serve very different purposes.
- Nofollow: This attribute is applied to individual links and tells search engines not to follow the link or pass any ranking value to the linked page.
- Noindex: This is a metatag that you apply at the page level. When you use the noindex tag on a page, it instructs search engines not to index that page, meaning it won’t appear in search results at all.
In short, if you want to prevent search engines from indexing a particular page, you need to use the noindex tag. A nofollow link won’t do the job in that case-it only stops search engines from following the link.
Nofollow Link Attribute Vs. Meta Robots Nofollow
It’s important to distinguish between the nofollow link attribute and the meta robots nofollow directive, as they have different effects on a page.
- Nofollow Link Attribute: This applies only to a specific link on a page. It instructs search engines not to follow that particular link, but it doesn’t impact other links on the same page.
- Meta Robots Nofollow Directive: This, on the other hand, is applied at the page level. When you include the meta robots nofollow directive in your page’s source code, it signals to search engines not to follow any links on the page.
Here’s an example of what the meta robots nofollow directive looks like in your page’s source code:
<meta name="robots" content="nofollow">
Using this directive means that every link on the page will be treated as a nofollow link, potentially having a much broader impact on your site’s link profile.
By understanding the differences between these tags and directives, you can make informed decisions on how to manage your site’s links and search engine visibility.
Types Of Nofollow Links And When To Apply Them
There are three primary "rel" attributes that signal to Google the relationship between your site and the page you’re linking to. These attributes-used either individually or combined-provide clear instructions on how search engines should treat the links. You can combine them by separating each attribute with a space or comma.
Note: While Google encourages using specific link attributes like “sponsored” or “UGC” (user-generated content), it’s perfectly fine to use rel="nofollow" in these instances. However, Google prefers site owners to be explicit about the type of link, likely to help improve its algorithm’s understanding and detection.
Sponsored Links: rel="sponsored"
If you’re selling links on your site, such as through ads or paid partnerships, you must label these links appropriately so that Google knows not to pass PageRank (or “link equity”). Using the rel="sponsored" attribute ensures that the link is marked as paid or promotional content, preventing it from influencing search rankings.
Here’s an example of a sponsored link in HTML:
<a href="https://sponsorwebsite.com" rel="sponsored">Check out our sponsor</a>
Adding the rel="sponsored" tag to a link works the same way as rel="nofollow", but it provides Google with more specific information about the link’s purpose, making it clearer that the link is paid or promotional.
User-Generated Content: rel="ugc"
The rel="ugc" attribute is used to identify links in user-generated content, such as comments, forum posts, and reviews. Originally, the nofollow tag was used to prevent spammy links from passing SEO value, as some users and SEOs would abuse comment sections for backlinks.
Here’s an example of a UGC link in HTML:
<a href="https://usercontent.com" rel="ugc">Check out this user’s post</a>
Most content management systems (CMS) now automatically apply the rel="ugc" tag to any links added in comment sections or forums. This helps prevent link spam while still allowing users to share valuable content.
The Catch-All Option: rel="nofollow"
The rel="nofollow" attribute remains the most versatile of the three and can be used on any link where you don’t want to pass any SEO value. This attribute is ideal when you’re linking to pages that you can’t fully endorse or trust but still want to provide for user reference.
Here’s an example of a nofollow link in HTML:
<a href="https://randomwebsite.com" rel="nofollow">Visit random site</a>
Many major news outlets and online publications often use this tactic to blanket all external links with the nofollow attribute. While it’s a common practice to avoid potential Google penalties, this approach is not ideal for editorial links. A better practice is to ask yourself, “If I don’t trust this link or site, why am I linking to it in the first place?”
In conclusion, using the appropriate “rel” attribute helps Google understand the intent behind your links and ensures that your site maintains a clean, transparent link profile.
Additional Uses Of The Nofollow Link Attribute
While the nofollow attribute is primarily applied to outbound links, it can also be useful for improving your internal site structure. For example, you can use nofollow links to control how search engines interact with internal pages, particularly those with filtered or faceted navigation.
Faceted navigation often generates multiple URLs with near-duplicate content, which can overwhelm search engines with unnecessary pages to crawl. By adding the nofollow attribute to links that apply filter parameters (such as color or size), you can prevent search engines from following these URLs. Here’s an example of a nofollow link applied to a filtered product page for socks:
<a href="https://example.com/socks/?color=black" rel="nofollow">Black</a>
In this case, the main socks category remains indexed, but the nofollow attribute stops search engines from crawling all the filtered variations (like different colors), reducing the risk of duplicate content.
If other websites link to your filtered pages, search engines can still find and crawl them. Additionally, Google now treats the nofollow attribute as a “hint” rather than a strict directive. If avoiding filtered page crawling is critical, it’s better to use disallow directives in your robots.txt file for more reliable control.
How To Implement Nofollow Backlinks On Your Site
Wondering how to add nofollow links to your website? The process varies depending on the platform or CMS your site is built on.
For WordPress users, good news: by default, all comment section links are automatically assigned the nofollow attribute to help prevent spammy backlinks. Moreover, you can find several plugins that allow you to mark all your external links as nofollow, making it easy to manage them sitewide.
If your site is custom-built or uses another platform, you may need to manually add the rel="nofollow" attribute to specific external links. In this case, it’s a good idea to work with a developer to ensure all necessary links are properly tagged.
Should You Mark External Links As Nofollow?
Now comes the question: should you apply the nofollow attribute to external links on your site? Let’s break it down.
First, if you’re using a CMS like WordPress, keep in mind that some links, such as those in blog comments, will automatically be marked as nofollow. This is done to prevent spammy link-building in comments, so you don’t need to intervene.
Second, Google strongly recommends that webmasters mark paid links and advertisements with the nofollow attribute. This includes affiliate links or any paid placements on your site. Not marking these links appropriately could lead to penalties, as Google wants to ensure these links don’t influence search engine rankings unfairly.
For websites with lots of outgoing links-especially blogs with guest authors or curated content-you may want to strike a balance between nofollow and standard (dofollow) links. This approach creates a more natural-looking link profile and reduces the risk of being penalized for hosting low-quality dofollow links.
On the other hand, if your site has relatively few external links and no paid content, you may not need to worry about using the nofollow attribute as much. In this case, your linking strategy will likely be fine as is.
Finally, conducting a comprehensive SEO audit or backlink analysis can help identify any areas where you might need to adjust your internal and external linking practices. If you’re unsure where to start or need expert advice, we’re here to assist you!
Does Google Recognize Nofollow Bacllinks?
In 2019, Google announced a significant change to how it handles nofollow links, marking the first major shift in nearly 15 years. Starting in March 2020, Google stated that nofollow attributes would no longer be treated as strict directives but rather as “hints.”
This means that:
- Nofollow links could serve as a hint for crawling or indexing.
- Nofollow links might also be used as a hint for ranking purposes.
The change was widely seen as Google’s way of accounting for trusted publications that were applying nofollow to all external links by default. With this update, nofollow links from reputable sites could still influence rankings, meaning that even nofollow links from high-quality sources might indirectly benefit your SEO.
Should I Use Nofollow Backlinks For Internal Pages?
Google has clarified that while the nofollow attribute is now treated as a hint for crawling and indexing, its use internally remains optional. John Mueller from Google stated:
“It’s not 100% defined, but the idea is that using internal nofollow links tells Google which pages are less important, signaling that they don’t need to be crawled or ranked.”
There’s no penalty for using nofollow on internal links, and it can be useful for signaling that certain pages-like login or checkout pages-are not essential for SEO.
Many websites commonly apply nofollow to:
- Login pages
- Register pages
- Cart/checkout pages
However, when optimizing your site, always weigh the cost of implementation against the expected benefits to ensure efficient use of resources.
4 Free Extensions To Identify Nofollow Backlinks
Identifying nofollow links on a webpage can be tricky without the right tools. Luckily, several browser extensions make this task simple by highlighting nofollow links directly on the page. Here are four free extensions that can help you quickly spot nofollow links.

NoFollow Simple (Chrome)
NoFollow Simple is a lightweight Chrome extension that highlights all nofollow links on a webpage by outlining them with a red dotted border. It’s perfect for users who want a straightforward tool without unnecessary features. Once activated, it works automatically on any page you visit, making nofollow links easy to spot at a glance.
SEOquake (Chrome and Firefox)
SEOquake is a powerful SEO tool that provides a wealth of information, including the ability to identify nofollow links. When enabled, it highlights nofollow links in a specific color, allowing you to see them instantly. In addition to spotting nofollow links, SEOquake offers other SEO insights like page analysis and keyword density, making it an all-in-one solution.
Check My Links (Chrome)
Check My Links is primarily a broken link checker, but it also highlights nofollow links on the page. When you run the extension, it will scan all the links on a webpage and mark nofollow links in yellow, making them easy to identify. This tool is especially useful for SEO professionals who want to quickly assess link attributes and ensure that all external links are properly tagged.
Linkparser (Chrome)
Linkparser is a handy Chrome extension designed to analyze various link types on a webpage. It differentiates between dofollow and nofollow links by highlighting them in different colors. Nofollow links are usually highlighted in red, providing an instant visual cue. It’s an excellent choice for users who need a comprehensive link analysis tool.
These extensions offer a quick and easy way to identify nofollow links without having to dig into the HTML code, making them essential tools for anyone working on SEO or website optimization.
When To Avoid Nofollow Backlinks

There are a few instances where you should avoid using nofollow links, and they are quite straightforward.
For Most Internal Links
One major rule is to avoid applying nofollow to your internal links. Internal links should generally be dofollow to help with site navigation and SEO benefits, with few exceptions like duplicate content pages.
For Relevant External Websites
Avoid indiscriminately applying nofollow to all outbound links. When linking to reputable, high-quality external sites, using dofollow can be beneficial. It signals to Google that your site is connected to authoritative sources, which can enhance your credibility.
How To Manage Nofollow Backlinks
Managing nofollow backlinks is easy, especially if your site runs on WordPress. Here are a couple of methods to handle it effectively:
Editing Links Manually In The WordPress Classic Editor
In the WordPress classic editor, you can manually add the nofollow attribute to any link by following these steps:
- Create a new post or page.
- Add your anchor text and create the hyperlink.
- To make the link open in a new tab, adjust the link options.
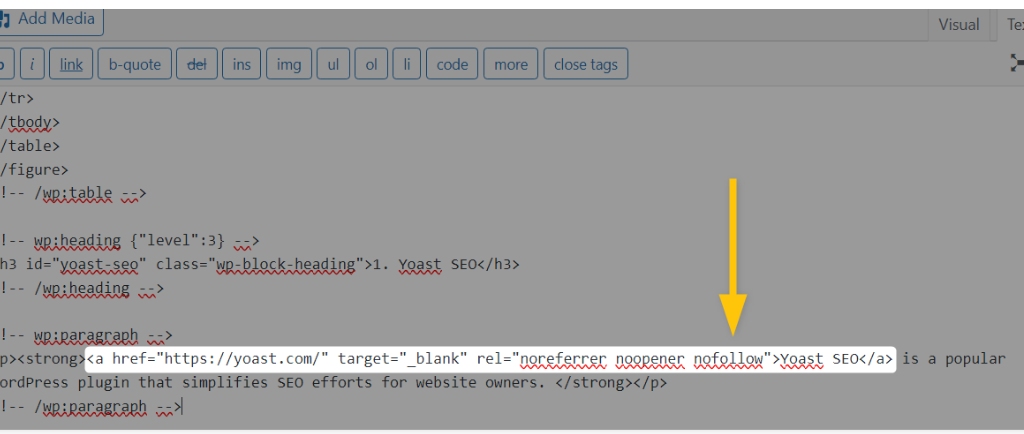
- Change the editor view to Text mode.
- Add
rel="nofollow"within the link’s HTML tag.
Using A WordPress Plugin
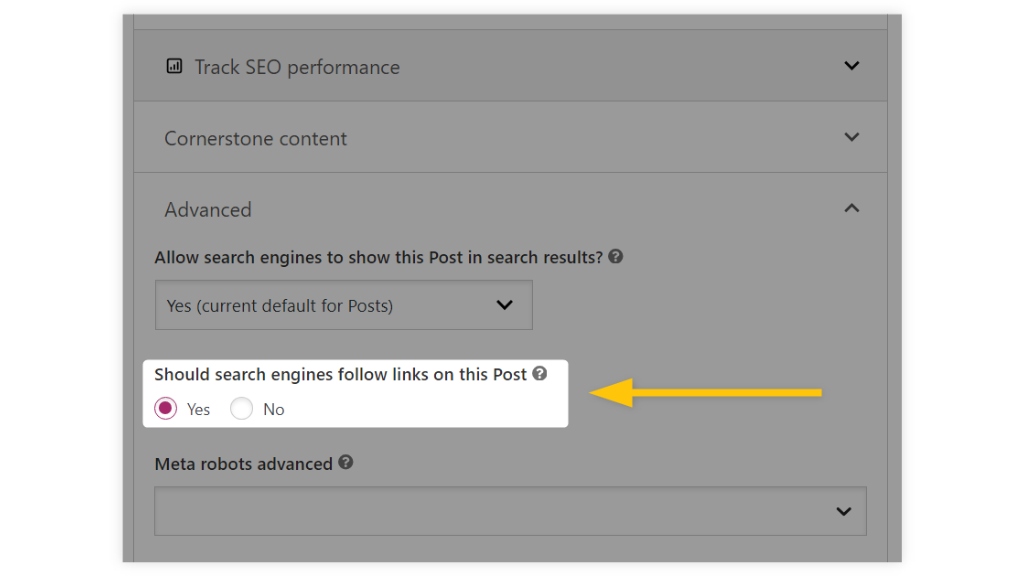
If you prefer automation, plugins like Yoast SEO or External Links make managing nofollow links easier. With Yoast SEO, you can:
- Apply the nofollow attribute sitewide or to individual links.
- Scroll down to the Yoast SEO plugin, click on the Advanced tab, and select the appropriate option for search engines to follow or not follow the links on a page.
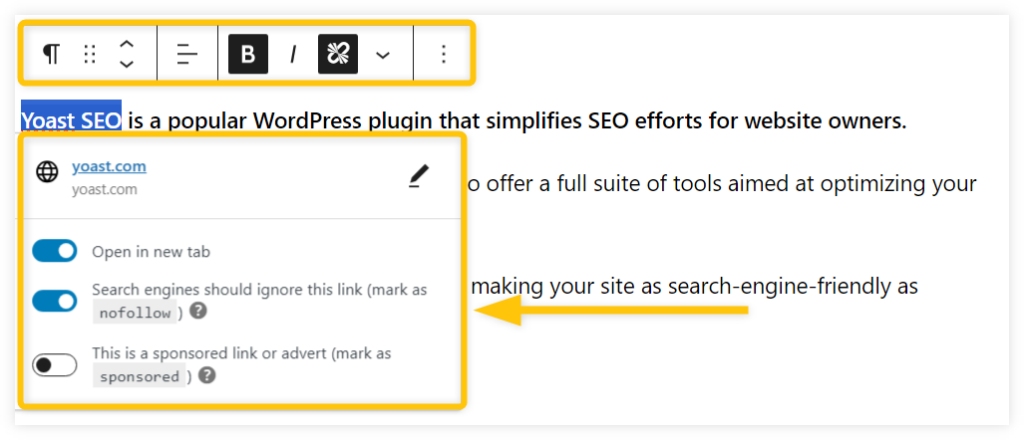
For individual links, simply:
- Highlight the anchor text in the WordPress editor.
- Click the link icon to add your URL.
- Choose the nofollow option from the dropdown.
The External Links plugin can also help you manage all external links on your site, adding nofollow automatically or by setting custom rules.
💡Tip: When linking to external sites, consider adding target="_blank" to open links in a new tab. This enhances the user experience by making it easier for visitors to return to your site after exploring an external link.
By carefully managing your nofollow links, you can strike the right balance between protecting your SEO while enhancing user navigation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, OctopusWriters has highlighted the importance of nofollow backlinks and provided practical examples and strategies for their effective use. Implementing nofollow links correctly on your website or blog helps safeguard your site from passing authority to spammy sites or competitors.
While search engines may not always consider nofollow links a direct ranking factor, they still offer significant value. By helping to create a balanced, natural backlink profile and driving traffic from reputable sources, nofollow links play a crucial role in supporting your overall SEO strategy and boosting visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions

What Is A Nofollow Link? |
Nofollow links are hyperlinks that include the rel="nofollow" HTML tag. This tag instructs search engines not to pass any ranking value or PageRank through that link. As a result, nofollow links typically don’t directly influence search engine rankings. |
Are Nofollow Backlinks Beneficial For SEO? |
| Yes, nofollow links can be beneficial for SEO, as they contribute to a natural backlink profile and can drive traffic, even if they don’t pass ranking value. |
How Can You Tell If A Link Is Nofollow? |
Inspect the link’s HTML code. If you see rel="nofollow" in the link tag, it is a nofollow link. |
Are Nofollow Backlinks Crawled? |
| Yes, Google may still crawl nofollow links. Although nofollow suggests that a link shouldn’t influence rankings, Google might still crawl and index pages connected by nofollow links, treating the tag as a “hint” rather than a strict directive. However, these pages might not perform well in rankings. |

